
Let’s Discuss, Metal Parts Manufactured By Extrusion 3d Printing
In the world of manufacturing, innovation is the name of the game. Traditional manufacturing methods have long dominated the industry, but the emergence of 3D printing has opened up a realm of possibilities previously unimaginable. Among the various techniques within the realm of 3D printing, one method stands out for its potential to reshape industries: metal parts 3D printing by extrusion.
Extrusion-based 3D printing, also known as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), has been predominantly associated with plastics. However, advancements in technology have paved the way for its application in metal printing, offering numerous benefits and opportunities for manufacturers across different sectors.
Understanding Metal Parts 3D Printing by Extrusion
At its core, metal parts 3D printing by extrusion operates on the same principles as its plastic counterpart. Instead of using thermoplastic filaments, this method employs metal filaments, typically composed of metal powders mixed with a thermoplastic binder.
The process begins with a CAD model sliced into layers, just like in traditional 3D printing. However, unlike plastics, metal filaments require significantly higher temperatures for extrusion. Specialized 3D printers equipped with powerful heating systems are employed to melt the metal filaments, which are then extruded layer by layer to build the desired object.
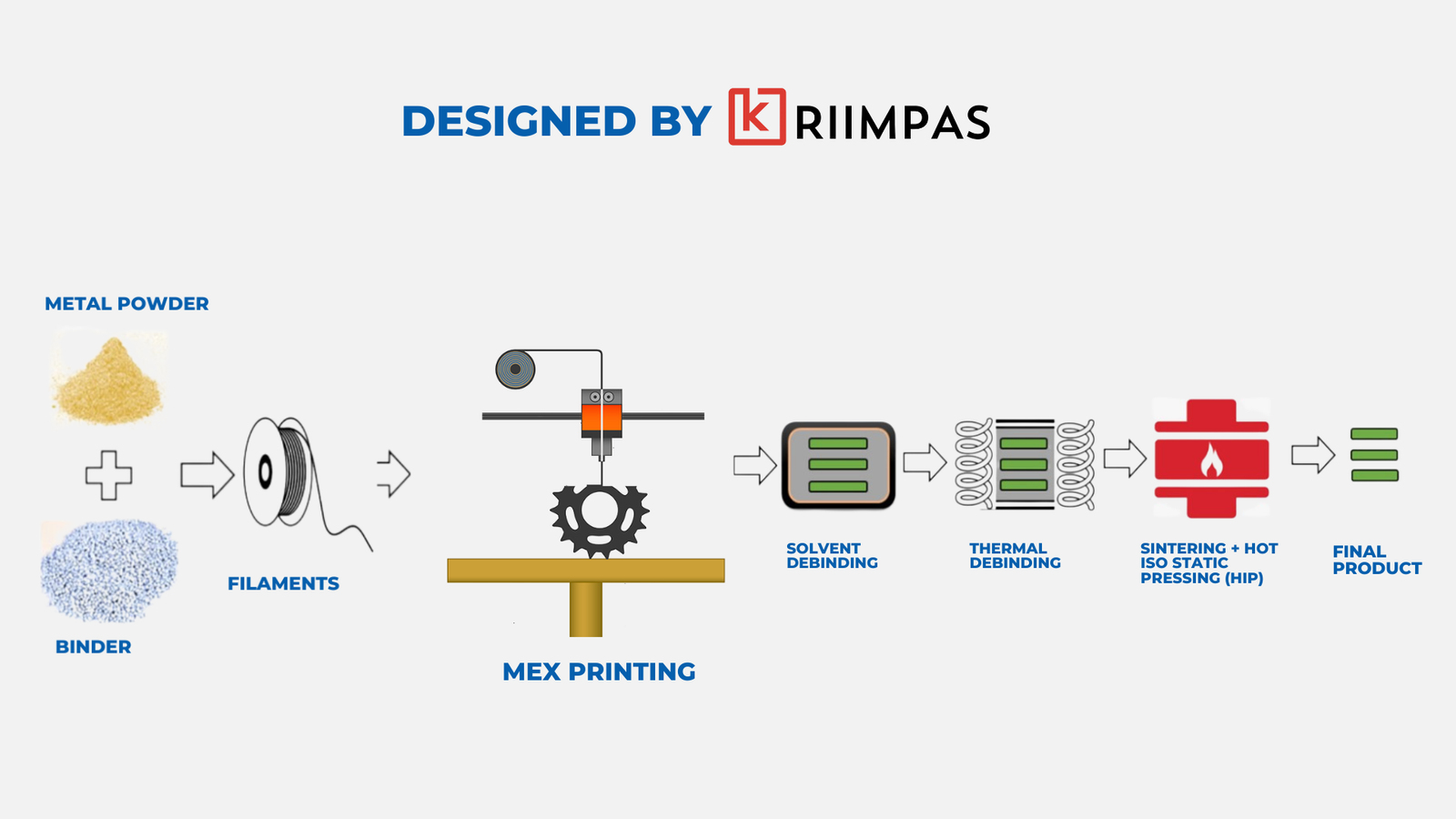
Advantages of Metal Parts 3D Printing by Extrusion
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to traditional metal manufacturing methods like CNC machining or casting, metal parts 3D printing by extrusion can be more cost-effective, especially for small to medium-sized production runs. The additive nature of 3D printing minimizes material waste, resulting in cost savings.
- Complex Geometries: One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing, regardless of material, is its ability to create complex geometries with ease. Metal parts 3D printing by extrusion is no exception. Manufacturers can produce intricate designs and assemblies that would be challenging or impossible to achieve using traditional methods.
- Customization and Prototyping: Rapid prototyping and customization are inherent strengths of 3D printing. With metal parts 3D printing by extrusion, manufacturers can quickly iterate designs and produce custom parts on-demand, reducing lead times and speeding up the product development cycle.
- Material Variety: While metal 3D printing encompasses various techniques, extrusion-based methods offer versatility in materials. From stainless steel and aluminum to titanium and copper, manufacturers have access to a wide range of metal filaments, each with its unique properties and applications.
- Reduced Tooling Requirements: Unlike conventional manufacturing processes that often require specialized tooling, metal parts 3D printing by extrusion eliminates the need for extensive tooling setups. This agility enables manufacturers to respond swiftly to design changes or production demands.
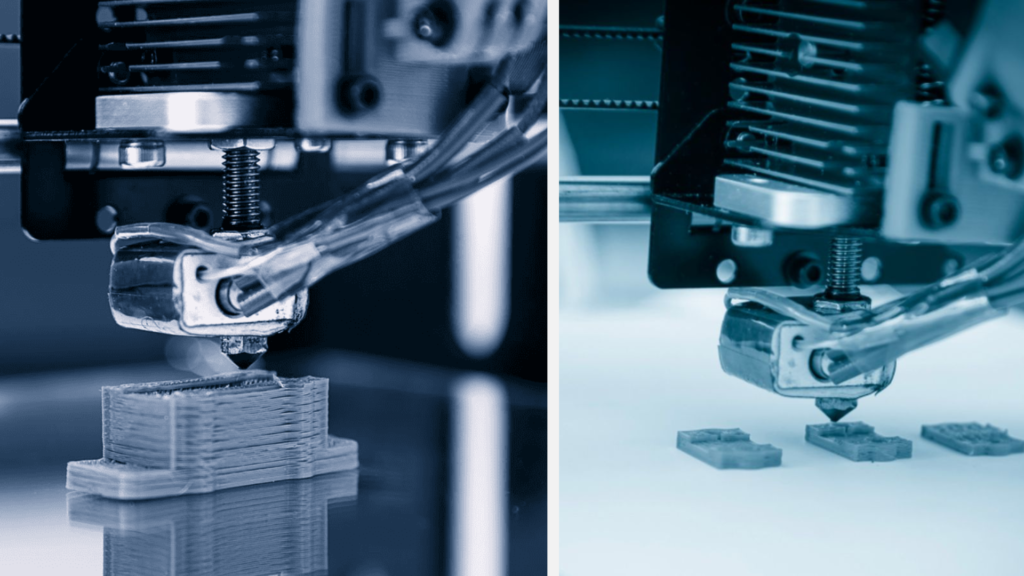
Have a Look
Understanding FDM 3D Printing:
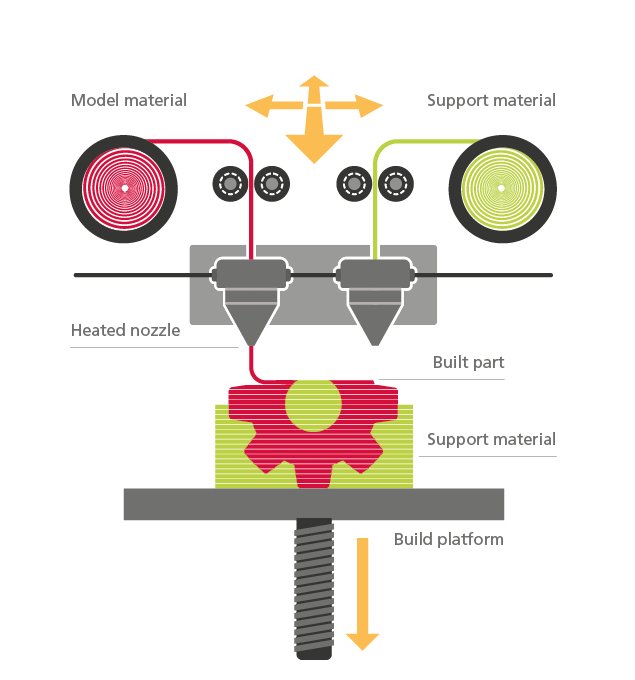
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), operates on a simple yet ingenious principle. It involves the extrusion of thermoplastic filament material through a heated nozzle, which deposits layers of material onto a build platform according to a computer-generated design.
The process begins with a digital model sliced into thin layers using specialized software. These slices serve as instructions for the 3D printer, dictating the precise path and deposition of the filament material layer by layer. As each layer is deposited and cooled, it fuses with the previous layer, gradually building up the desired object.
Conclusion: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing continues to push the boundaries of innovation, offering cost-effective, efficient, and versatile solutions for a wide range of applications across industries. As technology advances and new materials emerge, the future of FDM holds exciting possibilities, from multi-material printing to large-scale production, driving further adoption and innovation in the world of additive manufacturing.
Understanding Paste 3d Printing :
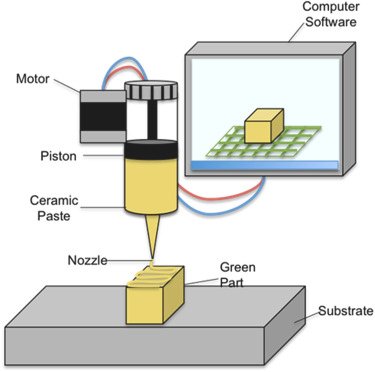
Paste 3D printing, also known as extrusion-based or volumetric 3D printing, involves the deposition of viscous materials through a nozzle onto a build platform to create layered structures. Unlike traditional 3D printing, which relies on solid filaments or powders, paste printing utilizes materials with a paste-like consistency, such as ceramics, polymers, bioinks, and food-based substances.
The process begins with a digital model sliced into layers, similar to other additive manufacturing techniques. However, instead of melting or sintering solid materials, paste 3D printers extrude layers of viscous paste onto the build platform. Each layer is carefully deposited and cured or solidified, either through chemical reactions, heat, or exposure to light, depending on the material being used.
Conclusion: Paste 3D printing represents a paradigm shift in additive manufacturing, offering a versatile and sustainable approach to fabricating complex structures and functional objects. With its diverse material options, customization capabilities, and potential applications across industries, paste printing holds immense promise for the future of manufacturing, biomedicine, architecture, and beyond. As research and development efforts continue to drive innovation, we can expect to see paste 3D printing play an increasingly significant role in shaping the world of tomorrow.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility and benefits of metal parts 3D printing by extrusion have led to its adoption across diverse industries:
- Aerospace: From lightweight structural components to intricate engine parts, 3D-printed metal components are revolutionizing aerospace manufacturing by offering improved performance and fuel efficiency.
- Automotive: Automotive manufacturers leverage metal parts 3D printing for prototyping, tooling, and producing lightweight yet durable components, enhancing vehicle efficiency and performance.
- Medical: In the medical sector, 3D-printed metal implants and prosthetics offer personalized solutions tailored to individual patients, improving outcomes and patient satisfaction.
- Industrial Manufacturing: From machinery components to specialized tooling, metal parts 3D printing by extrusion enhances efficiency and enables on-demand production, minimizing downtime and streamlining operations.
Future Outlook
As technology continues to evolve, the future of metal parts 3D printing by extrusion looks promising. Ongoing research and development efforts focus on enhancing print speeds, improving material properties, and expanding the range of printable metals. With each advancement, the capabilities of extrusion-based metal 3D printing are further strengthened, unlocking new possibilities and applications across industries.
In conclusion, metal parts 3D printing by extrusion represents a transformative shift in manufacturing, offering cost-effective, customizable, and efficient solutions for producing complex metal components. As adoption rates rise and technology advances, we can expect to see this innovative manufacturing method play an increasingly significant role in shaping the future of industry, Apart from extrusion 3d printing, metal parts can be made by Direct energy deposition (DED) and by binder jetting.

